Machine
From The Art and Popular Culture Encyclopedia
| Revision as of 16:55, 26 June 2012 Jahsonic (Talk | contribs) ← Previous diff |
Current revision Jahsonic (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | [[Image:Mechanic.jpg|thumb|200px|right|"[[Powerhouse mechanic working on steam pump]]," [[1920]]]] | + | [[Image:Mechanic.jpg|thumb|200px|left|"[[Powerhouse mechanic working on steam pump]]," 1920]] |
| - | [[Image:Duck of Vaucanson.jpg|thumb|200px| | + | {| class="toccolours" style="float: left; margin-left: 1em; margin-right: 2em; font-size: 85%; background:#c6dbf7; color:black; width:30em; max-width: 40%;" cellspacing="5" |
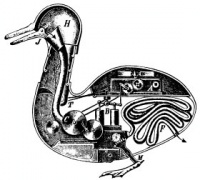
| - | <small>The '''''Canard Digérateur''''', or '''Digesting Duck''', was an [[automaton]] in the form of [[duck]], created by [[Jacques de Vaucanson]] in [[1739]]. | + | | style="text-align: left;" | |
| - | Voltaire wrote that "without [...] the duck of [[Vaucanson]], you have nothing to remind you of the glory of [[France]]." (''"Sans...le canard de Vaucanson vous n'auriez rien qui fit ressouvenir de la gloire de la France."'') This is often misquoted as "Without the shitting duck, we would have nothing to remind us of the glory of France."</small>]] | + | "When people in the early [[seventeenth century]] talk of 'machines' they usually mean [[theatrical machines]]."--''[[Theatre of the World]]'' (1969) by Frances Yates |
| - | [[Image:Homme machine (1747) - Julien Offray de La Mettrie.jpg|right|thumb|200px|''[[Man a Machine]]'' ([[1747]]) by [[Julien Offray de La Mettrie]] (edition shown [[1750]])]] | + | <hr> |
| - | {{Template}} | + | "But I can see you!" she exclaimed. "What more do you want?"<br> |
| - | # a [[mechanical]] or [[electrical]] device that performs or assists in the performance of human tasks, or is used for amusement (like a pinball machine). | + | "I want to see you not through the [[Machine]]," said Kuno. "I want to speak to you not through the wearisome Machine."<br> |
| - | # the group that controls a political or similar organization. | + | "Oh, hush!" said his mother, vaguely shocked. "You mustn"t say anything against the Machine."<br> |
| - | # a vehicle operated mechanically; an [[automobile]]. | + | "Why not?"<br> |
| - | # a person who seemingly acts like a machine, a person who is very [[proficient]] at a [[task]]. | + | "One mustn"t."<br> |
| - | #: ''Bruce Campbell was a "demon-killing machine" because he made quick work of killing demons.'' | + | |
| - | == Types and related components == | + | --"[[The Machine Stops]]" (1909) by E.M. Forster |
| - | {| class="wikitable" | + | |
| - | |+ Types of machines and related components | + | |
| - | ! rowspan="1" colspan="2" | Classification !! Machine(s) | + | |
| - | |- | + | |
| - | | rowspan="1" colspan="2" | [[Simple machine]]s || [[Inclined plane]], [[Wheel and axle]], [[Lever]], [[Pulley]], [[Wedge (mechanics)|Wedge]], [[Screw (simple machine)|Screw]] <!-- 'Simple machine' has a rather precise meaning - and that is the complete list - don't add to it! --> | + | |
| - | |- | + | |
| - | | rowspan="1" colspan="2" | Mechanical components || [[Axle]], [[Bearing (mechanical)|Bearings]], [[Belt (mechanical)|Belts]], [[Bucket (machine part)|Bucket]], [[Fastener]], [[Gear]], [[Key (lock)|Key]], [[Link chain]]s, [[Rack and pinion]], [[Roller chain]]s, [[Rope]], [[Seal (mechanical)|Seals]], [[Spring (device)|Spring]], [[Wheel]] | + | |
| - | |- | + | |
| - | | rowspan="1" colspan="2" | [[Clock]] || [[Atomic clock]], [[Chronometer]], [[Pendulum clock]], [[Quartz clock]] | + | |
| - | |- | + | |
| - | | rowspan="1" colspan="2" | [[Gas compressor|Compressors]] and [[Pump]]s || [[Archimedes' screw]], [[Eductor-jet pump]], [[Hydraulic ram]], [[Pump]], [[Tuyau]], [[Vacuum pump]] | + | |
| - | |- | + | |
| - | | rowspan="2" colspan="1" | [[Heat engine]]s || [[External combustion engine]]s || [[Steam engine]], [[Stirling engine]] | + | |
| - | |- | + | |
| - | | [[Internal combustion engine]]s || [[Reciprocating engine]], [[Gas turbine]] | + | |
| - | |- | + | |
| - | | rowspan="1" colspan="2" | [[Heat pump]]s || [[Absorption refrigerator]], [[Thermoelectric cooling|Thermoelectric refrigerator]], [[Regenerative cooling]] | + | |
| - | |- | + | |
| - | | rowspan="1" colspan="2" | [[Linkage (mechanical)|Linkages]] || [[Pantograph]], [[Cam]], [[Peaucellier-Lipkin linkage|Peaucellier-Lipkin]] | + | |
| - | |- | + | |
| - | | rowspan="1" colspan="2" | [[Turbine]] || [[Gas turbine]], [[Jet engine]], [[Steam turbine]], [[Water turbine]], [[Wind generator]], [[Windmill]] | + | |
| - | |- | + | |
| - | | rowspan="1" colspan="2" | [[Airfoil|Aerofoil]] || [[Sail]], [[Wing]], [[Rudder]], [[Flap (aircraft)|Flap]], [[Propeller]] | + | |
| - | |- | + | |
| - | | rowspan="1" colspan="2" | [[Electronics|Electronic devices]] || [[Vacuum tube]], [[Transistor]], [[Diode]], [[Resistor]], [[Capacitor]], [[Inductor]], [[Memristor]], [[Semiconductor]], [[Computer]] | + | |
| - | |- | + | |
| - | | rowspan="1" colspan="2" | [[Robot]]s || [[Actuator]], [[Servo motor|Servo]], [[Servomechanism]], [[Stepper motor]], [[Computer]] | + | |
| - | |- | + | |
| - | | rowspan="1" colspan="2" | Miscellaneous || [[Vending machine]], [[Wind tunnel]], [[Check weigher|Check weighing machines]], [[Riveting machines]] | + | |
| - | |- | + | |
| |} | |} | ||
| + | [[Image:Train wreck at Montparnasse 1895.jpg|thumb|right|200px|''[[Train wreck at Montparnasse]]'']] | ||
| + | [[Image:Duck of Vaucanson.jpg|thumb|200px|The '''''[[Canard Digérateur]]''''']] | ||
| + | [[Image:Homme machine (1747) - Julien Offray de La Mettrie.jpg|right|thumb|200px|''[[Man a Machine]]'' (1747) by Julien Offray de La Mettrie]] | ||
| + | {{Template}} | ||
| + | A '''machine''' is a [[tool]] consisting of one or more parts that is constructed to achieve a particular [[goal]]. Machines are [[Work (physics)|powered]] devices, usually [[mechanic]]ally, chemically, thermally or electrically powered, and are frequently [[motor]]ized. Historically, a device required moving parts to classify as a machine; however, the advent of [[electronics|electronics technology]] has led to the development of devices without moving parts that are considered machines. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The word "machine" is derived from the [[Latin]] word ''machina'', which in turn derives from the [[Doric Greek]] ''μαχανά'' (machana), [[Ionic Greek]] ''μηχανή'' (mechane) "contrivance, machine, engine" and that from ''[[μῆχος]]'' (mechos), "means, expedient, remedy". The meaning of machine is traced by the Oxford English Dictionary to something that has been constructed. This includes human design into the meaning of machine. | ||
| + | |||
| + | A [[simple machine]] is a device that simply transforms the direction or magnitude of a [[force]], but a large number of more complex machines exist. Examples include [[vehicle]]s, [[electronic system]]s, [[molecular machine]]s, [[computer]]s, [[television]] and [[radio]]. | ||
| == See also == | == See also == | ||
| - | *[[Animal machine]] | + | * [[All Watched Over by Machines of Loving Grace]] |
| - | *[[Man machine]] | + | * [[Animal machine]] |
| - | *[[Living machine]] | + | * ''[[The Machine Stops]]'' |
| - | *[[Simple machine]] | + | |
| - | *The [[Machine Age]] | + | |
| - | *''[[The Machine Stops]]'' | + | |
| * [[Darwin Among the Machines]] | * [[Darwin Among the Machines]] | ||
| * [[Desiring-production]] | * [[Desiring-production]] | ||
| + | * [[Ghost in the machine]] | ||
| * [[History of technology]] | * [[History of technology]] | ||
| * [[Human body]] | * [[Human body]] | ||
| + | * [[Living machine]] | ||
| + | * [[Machine (band)]] | ||
| + | * [[Machine types and related components]] | ||
| + | * [[Machine Age]] | ||
| + | * [[Man machine]] | ||
| + | * [[Rube Goldberg machine]] | ||
| + | * [[Simple machine]] | ||
| * [[Technology]] | * [[Technology]] | ||
| - | *[[Machine types and related components]] | + | * [[Useless machine]] |
| {{GFDL}} | {{GFDL}} | ||
Current revision
|
"When people in the early seventeenth century talk of 'machines' they usually mean theatrical machines."--Theatre of the World (1969) by Frances Yates "But I can see you!" she exclaimed. "What more do you want?" --"The Machine Stops" (1909) by E.M. Forster |
_-_Julien_Offray_de_La_Mettrie.jpg)
|
Related e |
|
Featured: |
A machine is a tool consisting of one or more parts that is constructed to achieve a particular goal. Machines are powered devices, usually mechanically, chemically, thermally or electrically powered, and are frequently motorized. Historically, a device required moving parts to classify as a machine; however, the advent of electronics technology has led to the development of devices without moving parts that are considered machines.
The word "machine" is derived from the Latin word machina, which in turn derives from the Doric Greek μαχανά (machana), Ionic Greek μηχανή (mechane) "contrivance, machine, engine" and that from μῆχος (mechos), "means, expedient, remedy". The meaning of machine is traced by the Oxford English Dictionary to something that has been constructed. This includes human design into the meaning of machine.
A simple machine is a device that simply transforms the direction or magnitude of a force, but a large number of more complex machines exist. Examples include vehicles, electronic systems, molecular machines, computers, television and radio.
See also
- All Watched Over by Machines of Loving Grace
- Animal machine
- The Machine Stops
- Darwin Among the Machines
- Desiring-production
- Ghost in the machine
- History of technology
- Human body
- Living machine
- Machine (band)
- Machine types and related components
- Machine Age
- Man machine
- Rube Goldberg machine
- Simple machine
- Technology
- Useless machine