Medicine
From The Art and Popular Culture Encyclopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Revision as of 20:57, 21 April 2013 Jahsonic (Talk | contribs) ← Previous diff |
Revision as of 20:58, 21 April 2013 Jahsonic (Talk | contribs) Next diff → |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
| :''[[pill]]'' | :''[[pill]]'' | ||
| - | '''Medicine''' is the [[science]] and [[art]] of [[healing]]. It encompasses a range of [[health care]] practices evolved to maintain and restore [[health]] by the [[prevention (medical)|prevention]] and [[therapy|treatment]] of [[illness]]. Before scientific medicine, healing arts were practiced in accordance with [[alchemy|alchemist]] treatments in accordance with [[ritual]] practices that developed out of [[religion]] and cultural [[tradition]]. The term "Western medicine" was until recently used to refer to scientific and science-based practices, to distinguish them from "[[Eastern medicine]]" —which are typically based in traditional, anecdotal, or otherwise non-scientific practices. | + | '''Medicine''' is the [[applied science]] or practice of the [[diagnosis]], [[healing|treatment]], and prevention of [[disease]]. It encompasses a variety of [[health care]] practices evolved to maintain and restore [[health]] by the [[prevention (medical)|prevention]] and [[therapy|treatment]] of [[illness]] in [[human beings]]. |
| - | Contemporary medicine applies [[health science]], [[biomedical research]], and [[medical technology]] to [[diagnosis (medical)|diagnose]] and treat [[injury]] and [[disease]], typically through [[medication]], [[surgery]], or some other form of [[therapy]]. The word ''medicine'' is derived from the [[Latin]] ''ars medicina'', meaning ''the art of healing''. | + | Contemporary medicine applies [[health science]], [[biomedical research]], and [[medical technology]] to [[diagnosis (medical)|diagnose]] and treat injury and disease, typically through [[medication]] or [[surgery]], but also through therapies as diverse as [[psychotherapy]], [[splint (medicine)|external splints & traction]], [[prostheses]], [[biologic medical product|biologics]], [[Radiation (medicine)|ionizing radiation]] and others. |
| - | Though medical technology and clinical expertise are pivotal to contemporary medicine, successful face-to-face relief of actual [[suffering]] continues to require the application of ordinary human [[feeling]] and [[compassion]], known in English as ''[[bedside manner]]''. | + | The word ''medicine'' is derived from the [[Latin]] ''ars medicina'', meaning ''the art of healing''. |
| == See also == | == See also == | ||
| *[[History of medicine]] | *[[History of medicine]] | ||
Revision as of 20:58, 21 April 2013
This page Medicine is part of the medicine series.
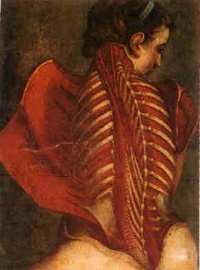
Illustration: The Flayed Angel (1746), anatomical drawing by Jacques Gautier d'Agoty
Illustration: The Flayed Angel (1746), anatomical drawing by Jacques Gautier d'Agoty
|
Related e |
|
Featured: |
Medicine is the applied science or practice of the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of disease. It encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention and treatment of illness in human beings.
Contemporary medicine applies health science, biomedical research, and medical technology to diagnose and treat injury and disease, typically through medication or surgery, but also through therapies as diverse as psychotherapy, external splints & traction, prostheses, biologics, ionizing radiation and others.
The word medicine is derived from the Latin ars medicina, meaning the art of healing.
See also
- History of medicine
- Disease
- Medical illustration
- Medical museum
- Medicine show
- Medicalization
- Anatomy
- Psychiatry
See also
- Surgery
- Neurosurgery
- Otolaryngology
- Transplant surgery
- Urology
- Allergy / Immunology
- Endocrinology
- Infectious disease
- Obstetrics and gynaecology
- Gynaecology
- Pathology
- Anesthesiology
- General practice
- Neurology
- Pain management
- Pediatrics
- Psychiatry
- Sexual medicine
- Physician
- Dentistry
- Veterinary medicine
- History of medicine
Unless indicated otherwise, the text in this article is either based on Wikipedia article "Medicine" or another language Wikipedia page thereof used under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License; or on research by Jahsonic and friends. See Art and Popular Culture's copyright notice.


